Self-monitoring of your diabetes
Diabetes is part of your everyday life. Appropriate self-monitoring can help you manage your daily blood glucose, and better adapt your lifestyle and treatment to suit your needs.1
The more often you check your blood glucose, the better you will understand it and the easier it will be for you to manage your diabetes. It doesn’t matter if you have type 1 or type 2 diabetes, or if you are taking insulin or not, self-monitoring can help you and your doctor manage your therapy.2
By managing your diabetes, you reduce the risk of developing complications. That means less eye, kidney and nerve damage, foot problems, and even stroke. Fewer complications means more time for you to enjoy your everyday life.
Adding structure to your self-monitoring
Self-monitoring allows you to track the levels of (high or low) blood glucose in your body, how particular foods affect you, and what happens after physical activity or taking medication.
You might find self-monitoring even more helpful if you do this in a structured way – by monitoring at the right times and in the right situations.
Structured self-monitoring can help you see a pattern that you and your doctor can use as part of your ongoing diabetes management.1
Your Accu-Chek® 360° View 3-day profile tool
To have a clear idea of how your blood glucose changes throughout the day and why, you should try and self-monitor seven times a day, for three days in a row by using the Accu-Chek 360° View profile tool.
Testing before you eat will tell you about the effect your medication has on your blood glucose, while testing 2 hours after you eat tells you about the effect of your meal. While using the Accu-Chek 360° View profiling tool you should test before and after breakfast, before and after lunch, before and after dinner, and once before you go to bed. You can then compare each day and use it to better manage your diabetes.
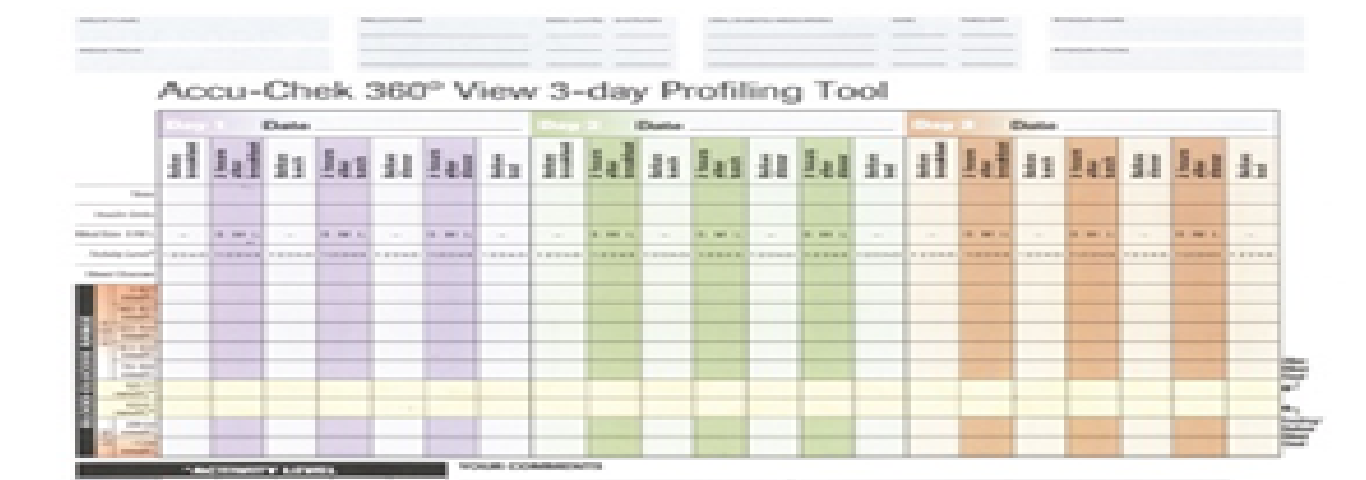
Download a PDF version of the Accu-Chek 3-day profile tool.
By self-monitoring your blood glucose you can measure how your body handles different types of food, exercise, medication, stress and illness. Your blood glucose result may prompt you to eat a snack, take more insulin or go for a walk. Self-monitoring can also alert you to a blood glucose level that is too high or too low, which requires special treatment.
Controlling your blood glucose level is a very important part of managing diabetes. Regularly testing your blood glucose helps measure the effectiveness of your meal plan, physical activity and medications.
Use the Accu-Chek 3-day profile tool as part of your self-monitoring routine to help guide you and your healthcare team when making adjustments to your therapy.
- Polonsky WH, et al. Diabetes Care 2011;34:262-7
- Self-Monitoring of Blood Glucose in Non-Insulin Treated Type 2 Diabtes. International Diabetes Federation. Available at www.idf.org/guidelines/self-monitoring Last accessed March 2012